Ergonomic Strategies for Managing Chronic Pain at Work
- E-Young Khoo
- Jan 9
- 3 min read
Chronic pain is a persistent issue that affects many workers, leading to decreased productivity, increased absenteeism, and reduced quality of life. For those who spend long hours at a desk, poor ergonomics can exacerbate chronic pain conditions, such as back pain, neck strain, and repetitive strain injuries. Implementing ergonomic strategies in the workplace can help manage and alleviate chronic pain, promoting a healthier and more productive work environment. In this blog post, we will explore effective ergonomic strategies for managing chronic pain at work.
Understanding the Impact of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is defined as pain that lasts for more than three months and can result from various conditions, including arthritis, musculoskeletal disorders, and nerve damage. It can lead to physical limitations, emotional distress, and decreased work performance. Addressing ergonomic factors in the workplace can significantly reduce the impact of chronic pain on employees.
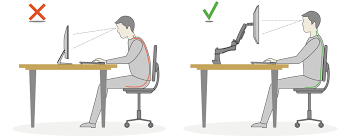
Key Ergonomic Strategies for Managing Chronic Pain
Proper Chair Selection:
Adjustable Features: Choose an ergonomic chair with adjustable height, lumbar support, and armrests. This allows for customization to fit the individual's body and reduce strain on the back and neck.
Lumbar Support: Ensure the chair provides adequate lumbar support to maintain the natural curve of the spine, reducing lower back pain.
Optimal Desk Setup:
Desk Height: Adjust the desk height so that your elbows are at a 90-degree angle when typing, with your wrists straight and relaxed.
Monitor Position: Place the monitor at eye level, about an arm's length away, to prevent neck strain and eye fatigue.
Keyboard and Mouse Placement:
Ergonomic Keyboard: Use an ergonomic keyboard to keep wrists in a neutral position, reducing the risk of repetitive strain injuries.
Mouse Position: Position the mouse close to the keyboard to minimise reaching and shoulder strain. Consider using an ergonomic mouse designed to reduce hand and wrist discomfort.
Supportive Foot Positioning:
Footrest: Use a footrest if your feet do not comfortably reach the floor. This helps maintain proper posture and reduces lower back strain.
Incorporate Movement and Stretching:
Frequent Breaks: Take short breaks every 20-30 minutes to stand, stretch, and move around. This helps reduce muscle stiffness and improves circulation.
Stretching Exercises: Incorporate gentle stretching exercises into your daily routine to alleviate muscle tension and improve flexibility.
Implement Sit-Stand Workstations:
Adjustable Desks: Consider using sit-stand desks that allow you to alternate between sitting and standing throughout the day. This can help reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and improve overall comfort.
Ergonomic Accessories:
Wrist Rests: Use wrist rests to support your wrists while typing, reducing strain and discomfort.
Document Holders: Use document holders to position reference materials at eye level, preventing neck strain.
Optimise Lighting:
Natural Light: Maximise natural light exposure to reduce eye strain and improve mood. Position workstations near windows and use blinds to control glare.
Task Lighting: Use adjustable desk lamps to provide focused lighting for specific tasks, ensuring even illumination across your workspace.
Promote a Healthy Work Environment:
Ergonomic Training: Provide ergonomic training and resources to employees to educate them on proper workstation setup and posture.
Wellness Programs: Implement workplace wellness programs that include ergonomic assessments, exercise routines, and mental health resources.
Managing chronic pain at work requires a combination of ergonomic strategies and proactive measures to create a comfortable and supportive work environment. By implementing ergonomic strategies, employees can significantly reduce the impact of chronic pain on their work performance and overall well-being.



Comments